Lung Cancer Symptoms
Lung cancer can happen to anyone. Men and women who smoke are about 25 times more likely to develop lung cancer than nonsmokers. But at least 20% of those diagnosed with lung cancer never smoked at all! Whether you’re young or old, a smoker or nonsmoker, it’s important to be on the lookout for lung cancer symptoms.

Early Lung Cancer Symptoms
As with most other cancers, lung cancer symptoms don’t always show until the cancer has become more advanced. However, that isn’t the case for everyone. Sometimes, a slight cough or shortness of breath, especially if you have never smoked, can be an early indication of lung cancer. And if these symptoms don’t clear up for anyone – smoker or nonsmoker – within a week or so or become more severe as time goes on, it’s a sign that you should see your doctor.
Lung cancer treatment, like most cancers, is more successful the earlier it’s diagnosed. Because of that, we recommend you contact your doctor if you are experiencing any of these lung cancer symptoms:
Unexplained hoarseness
Difficulty breathing
New onset of wheezing
A lingering cough not associated with a viral infection
Fatigue and/or weakness
Coughing up blood or coughing up spit or phlegm tainted with blood
Weight loss and loss of appetite not due to lifestyle changes
Recurring (chronic) infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia
Constant chest pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
Advanced Lung Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms often change once lung cancer becomes advanced and spreads to other areas of the body. Some advanced lung cancer symptoms may include:
Bone pain
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Lumps in the neck and/or collarbone region
A headache, dizziness, or weakness in the arms or legs
Often, many of the symptoms related to lung cancer are the result of something other than lung cancer. It’s less likely related to a virus or other short-term condition if the symptoms carry on for more than a week or two. See your doctor if you notice one or more of these signs or symptoms or anything unusual. Even if it’s not lung cancer, there are other conditions affecting the lungs that your doctor should look into for you.
Related Reading:
7 Surprising Signs & Symptoms of Lung Cancer That Don’t Involve the Lungs

Syndromes Caused By Lung Cancer
Some lung cancers can cause specific syndromes, which consist of a set of particular symptoms. Since these syndromes can affect other organs in the body, some doctors may misdiagnose and think something non-cancerous is causing the problem. These syndromes include:
Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS)
SVCS occurs when the major vein that carries blood from the head and arms back to the heart, is partially blocked or compressed. Common SVCS symptoms include shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, coughing, and swelling of the face, neck, upper body, and arms.
Horner syndrome
Horner syndrome is a set of symptoms caused by a disruption in the nerve pathway from the brain to the face and eye on one side of the body. Over time, people with Horner syndrome experience decreased pupil size, drooping or weakness of one eyelid, and little to no sweating on the affected side of the face.
Paraneoplastic syndrome
Paraneoplastic syndrome is a rare disorder caused by substances produced and secreted by a tumor. These substances can affect distant tissues and organs, even if the cancer has not spread to those areas. Some common paraneoplastic syndromes associated with lung cancer include:
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)
Cushing syndrome
Nervous system problems
Blood clotting issues
High blood calcium levels (hypercalcemia)
Excess growth or thickening of certain bones
Excess breast growth in men (gynecomastia)
Don’t Wait if You Notice Symptoms
Many symptoms of lung cancer, including syndromes, can be caused by conditions other than lung cancer. Even if you’re a little nervous about what the doctor will say, it’s important that you don’t put off an appointment. Schedule with your primary care physician, or, if you have a pulmonologist for other lung conditions they can also run tests to find the cause of your symptoms.
Several tests may be needed to provide a proper diagnosis.
Is Lung Cancer Screening Available?
Screening with a low-dose CT scan (LDCT) is an option for those people considered at high-risk for developing lung cancer. Screening tests are run annually which is why it’s only recommended for those with a history of smoking. For non-smokers the risk of repeated exposure to radiation from a CT scan outweighs the risk of of developing lung cancer.
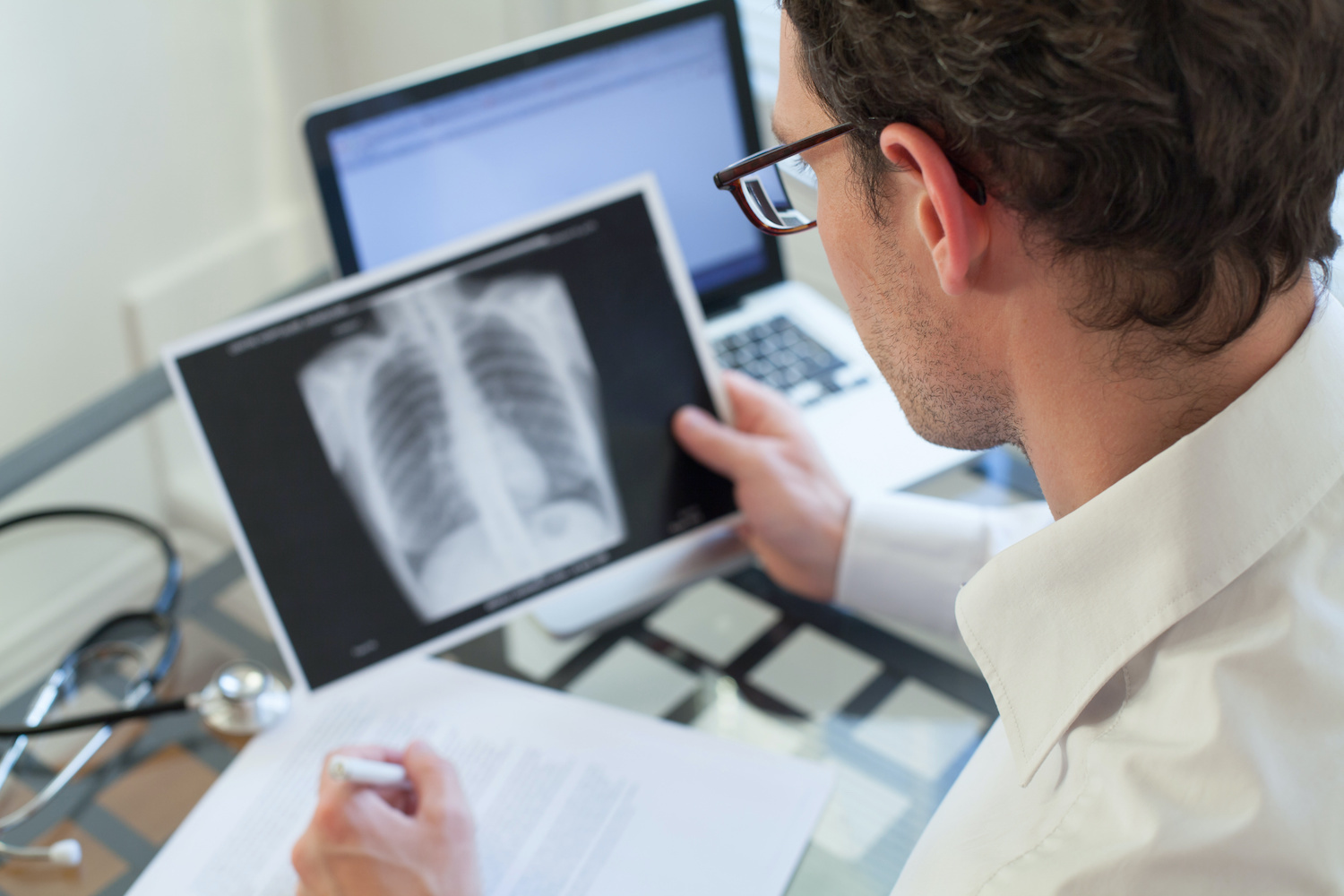
Lung cancer screenings are recommended for people who:
Are between 50 to 80 years old and in good health, and
Currently smoke or have quit smoking in the past 15 years, and
Have at least a "20-pack-year" smoking history
A pack-year is the number of packs of cigarettes smoked per day multiplied by the number of years smoked, which means that ten pack years could be from smoking a pack a day for 10 years or smoking two packs a day for five years.
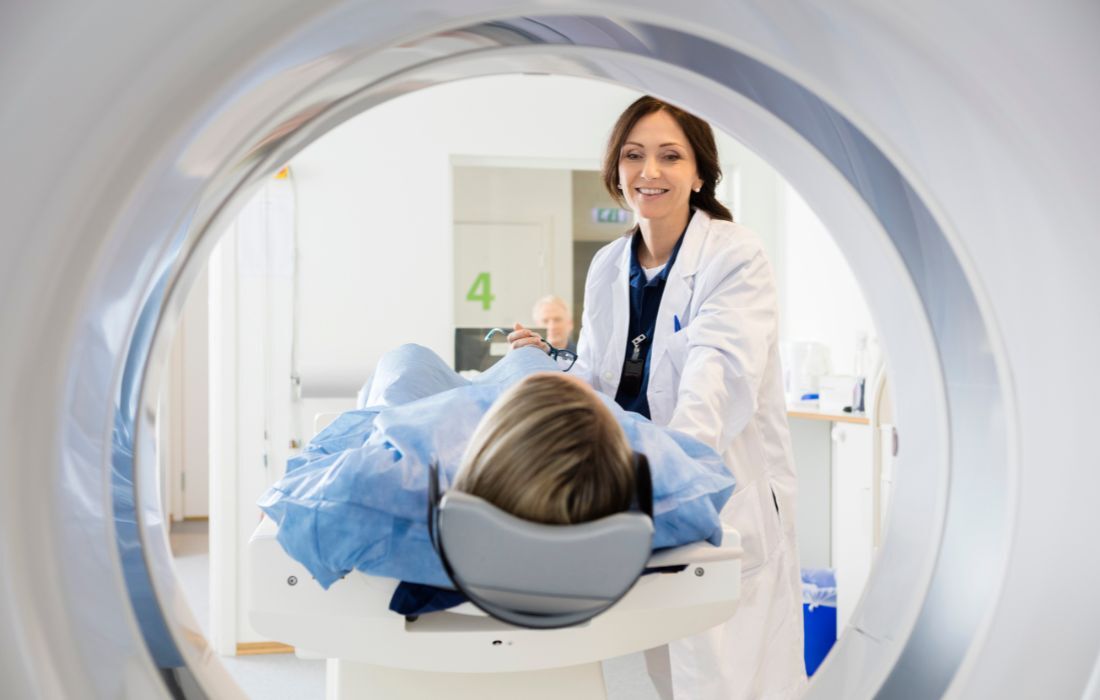
If screening shows signs of lung cancer, your doctor will discuss a biopsy next. That is the primary way to diagnose lung cancer. If you live in or around Brevard County, our lung cancer specialists can help. Contact Cancer Care Centers of Brevard to schedule an appointment at one of our convenient locations.